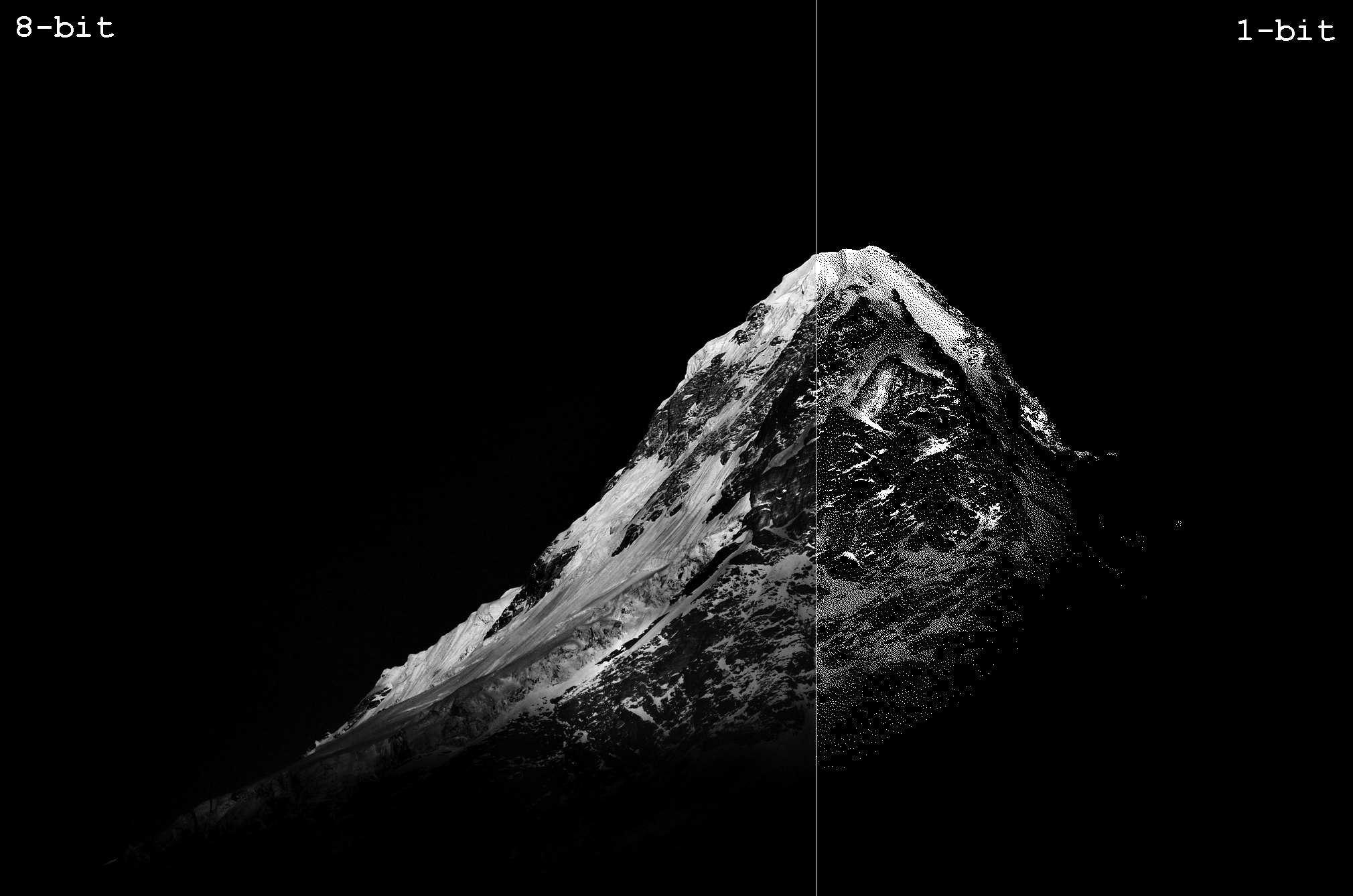
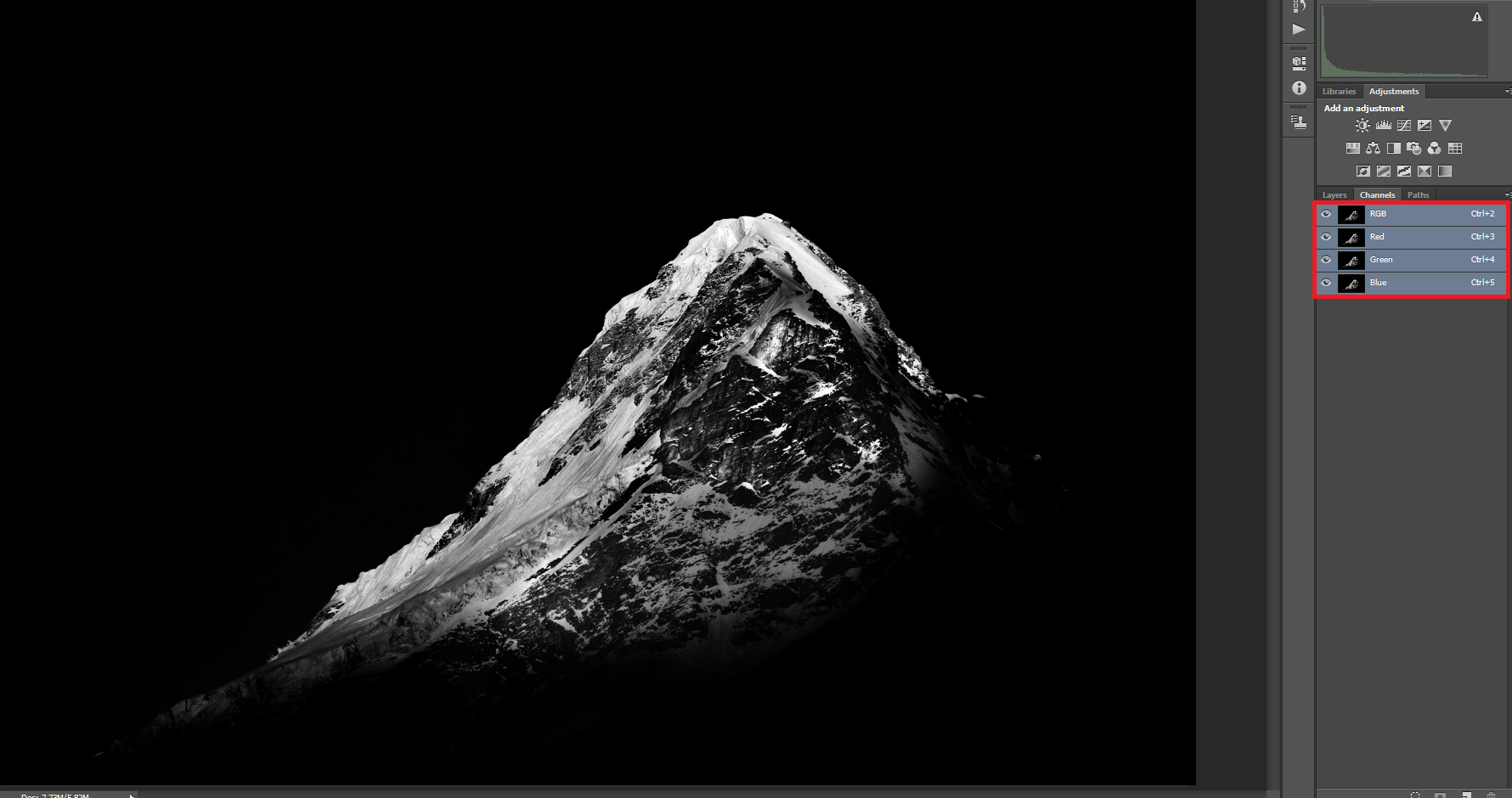
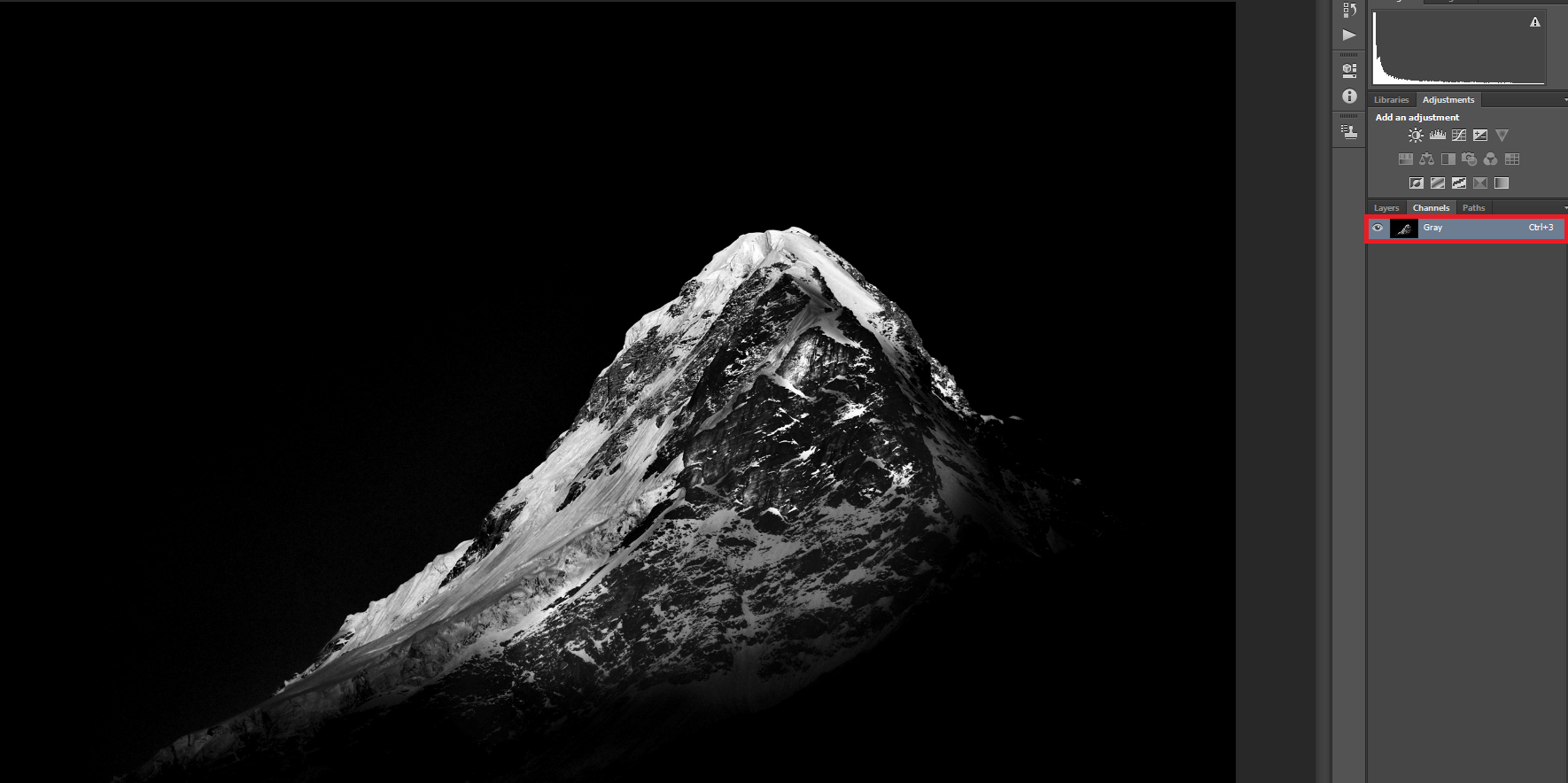
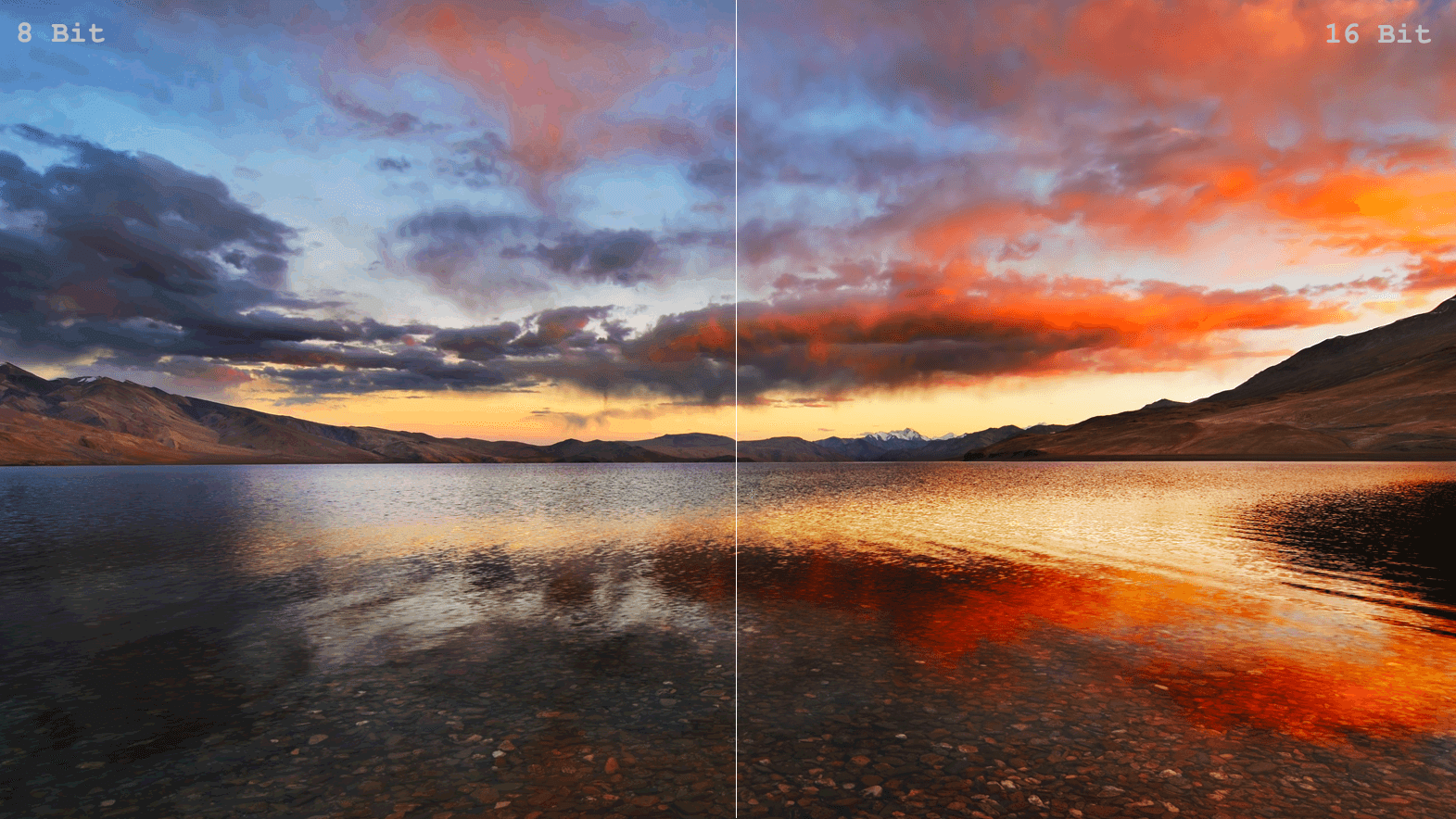
8-Bit vs 16-Bit Images
The term bit is common in any form of digital media. With respect to digital imaging, bit depth goes by many names like pixel depth or color depth. In digital photography, the debate of 8-bit vs 16-bit files has been going on as much as Nikon vs Canon. This article intends to give you a better understanding of what bit depth is. It will also take you through whether we need 16-bit images or not, and if we do, when we need them.
يعد مصطلح البت شائعًا في أي شكل من أشكال الوسائط الرقمية. فيما يتعلق بالتصوير الرقمي، فإن عمق البت يطلق عليه العديد من الأسماء مثل عمق البكسل أو عمق الألوان. في التصوير الفوتوغرافي الرقمي، يدور الجدل حول ملفات 8 بت مقابل 16 بت بقدر ما يحدث بين نيكون وكانون. تهدف هذه المقالة إلى تزويدك بفهم أفضل لعمق البت. وسوف يرشدك أيضًا إلى ما إذا كنا نحتاج إلى صور 16 بت أم لا، وإذا كنا نحتاج إليها، متى نحتاج إليها.
The term bit is common in any form of digital media. With respect to digital imaging, bit depth goes by many names like pixel depth or color depth. In digital photography, the debate of 8-bit vs 16-bit files has been going on as much as Nikon vs Canon. This article intends to give you a better understanding of what bit depth is. It will also take you through whether we need 16-bit images or not, and if we do, when we need them.
يعد مصطلح البت شائعًا في أي شكل من أشكال الوسائط الرقمية. فيما يتعلق بالتصوير الرقمي، فإن عمق البت يطلق عليه العديد من الأسماء مثل عمق البكسل أو عمق الألوان. في التصوير الفوتوغرافي الرقمي، يدور الجدل حول ملفات 8 بت مقابل 16 بت بقدر ما يحدث بين نيكون وكانون. تهدف هذه المقالة إلى تزويدك بفهم أفضل لعمق البت. وسوف يرشدك أيضًا إلى ما إذا كنا نحتاج إلى صور 16 بت أم لا، وإذا كنا نحتاج إليها، متى نحتاج إليها.







تعليق