فهم بطاقات الذاكرة
Understanding Memory Cards
بغض النظر عن الكاميرا الرقمية التي تقوم بالتصوير بها هذه الأيام، يجب أن يكون لديك نوع من التخزين حيث سيتم حفظ الوسائط الخاصة بك. على الرغم من أن بعض الأجهزة مثل الهواتف والأجهزة اللوحية غالبًا ما تأتي مزودة ببعض الذاكرة المدمجة، فستجد نفسك غالبًا تبحث عن طرق لتوسيع مساحة التخزين هذه باستخدام بطاقات الذاكرة أو ملحقات التخزين الخارجية الأخرى. وإذا قمت بالتصوير باستخدام كاميرا رقمية مخصصة، فستجد أنها لا توفر أي نوع من التخزين وستحتاج إلى شراء بطاقة ذاكرة واحدة على الأقل لتتمكن من تخزين الصور الملتقطة. هكذا يبدأ البحث عن أفضل بطاقة ذاكرة. يمكن أن يكون اختيار بطاقات الذاكرة تجربة محبطة للغاية، نظرًا لوجود العديد من أنواع بطاقات الذاكرة المختلفة التي تحتوي على العديد من الميزات ونقاط الأسعار المختلفة. وفي هذا المقال سنتعرف على بطاقات الذاكرة بالتفصيل ونقدم لك كل ما تريد معرفته عنها.
أولاً، سوف نقوم بتعريف بطاقات الذاكرة واستكشاف الأنواع المختلفة لبطاقات الذاكرة المتوفرة. ثم سنتناول الفئات المختلفة لبطاقات الذاكرة. وبعد ذلك سنوضح لك طرق كيفية قراءة وفهم المعلومات المكتوبة على بطاقات الذاكرة. وأخيرًا، سنقدم لك بعض النصائح والتوصيات حول اختيار بطاقات الذاكرة واستخدامها.
No matter what digital camera you shoot with nowadays, you must have some kind of storage where your media is going to be saved to. While some devices like phones and tablets often come with some built-in memory, you will often find yourself looking for ways to expand that storage by using memory cards or other external storage accessories. And if you shoot with a dedicated digital camera, you will find that it does not offer any kind of storage and you will need to buy at least one memory card in order to be able to store captured images. That’s how a quest for selecting the best memory card begins. Choosing memory cards can be a very frustrating experience, since there are so many different types of memory cards with so many different features and price points. In this article, we will explore memory cards in detail and give you everything you need to know about them.
First, we will define memory cards and explore the different types of memory cards available. Then we will go over the different classes of memory cards. After that, we will show you ways how to read and understand information written on memory cards. And lastly, we will give you some of our tips and recommendations on selecting and using memory cards.
Understanding Memory Cards
بغض النظر عن الكاميرا الرقمية التي تقوم بالتصوير بها هذه الأيام، يجب أن يكون لديك نوع من التخزين حيث سيتم حفظ الوسائط الخاصة بك. على الرغم من أن بعض الأجهزة مثل الهواتف والأجهزة اللوحية غالبًا ما تأتي مزودة ببعض الذاكرة المدمجة، فستجد نفسك غالبًا تبحث عن طرق لتوسيع مساحة التخزين هذه باستخدام بطاقات الذاكرة أو ملحقات التخزين الخارجية الأخرى. وإذا قمت بالتصوير باستخدام كاميرا رقمية مخصصة، فستجد أنها لا توفر أي نوع من التخزين وستحتاج إلى شراء بطاقة ذاكرة واحدة على الأقل لتتمكن من تخزين الصور الملتقطة. هكذا يبدأ البحث عن أفضل بطاقة ذاكرة. يمكن أن يكون اختيار بطاقات الذاكرة تجربة محبطة للغاية، نظرًا لوجود العديد من أنواع بطاقات الذاكرة المختلفة التي تحتوي على العديد من الميزات ونقاط الأسعار المختلفة. وفي هذا المقال سنتعرف على بطاقات الذاكرة بالتفصيل ونقدم لك كل ما تريد معرفته عنها.
أولاً، سوف نقوم بتعريف بطاقات الذاكرة واستكشاف الأنواع المختلفة لبطاقات الذاكرة المتوفرة. ثم سنتناول الفئات المختلفة لبطاقات الذاكرة. وبعد ذلك سنوضح لك طرق كيفية قراءة وفهم المعلومات المكتوبة على بطاقات الذاكرة. وأخيرًا، سنقدم لك بعض النصائح والتوصيات حول اختيار بطاقات الذاكرة واستخدامها.
No matter what digital camera you shoot with nowadays, you must have some kind of storage where your media is going to be saved to. While some devices like phones and tablets often come with some built-in memory, you will often find yourself looking for ways to expand that storage by using memory cards or other external storage accessories. And if you shoot with a dedicated digital camera, you will find that it does not offer any kind of storage and you will need to buy at least one memory card in order to be able to store captured images. That’s how a quest for selecting the best memory card begins. Choosing memory cards can be a very frustrating experience, since there are so many different types of memory cards with so many different features and price points. In this article, we will explore memory cards in detail and give you everything you need to know about them.
First, we will define memory cards and explore the different types of memory cards available. Then we will go over the different classes of memory cards. After that, we will show you ways how to read and understand information written on memory cards. And lastly, we will give you some of our tips and recommendations on selecting and using memory cards.












 Class 2 (C2)
Class 2 (C2) Class 4 (C4)
Class 4 (C4) Class 6 (C6)
Class 6 (C6)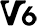 Class 6 (V6)
Class 6 (V6)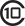 Class 10 (C10)
Class 10 (C10)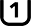 Class 1 (U1)
Class 1 (U1)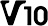 Class 10 (V10)
Class 10 (V10)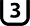 Class 3 (U3)
Class 3 (U3)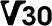 Class 30 (V30)
Class 30 (V30)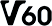 Class 60 (V60)
Class 60 (V60)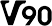 Class 90 (V90)
Class 90 (V90)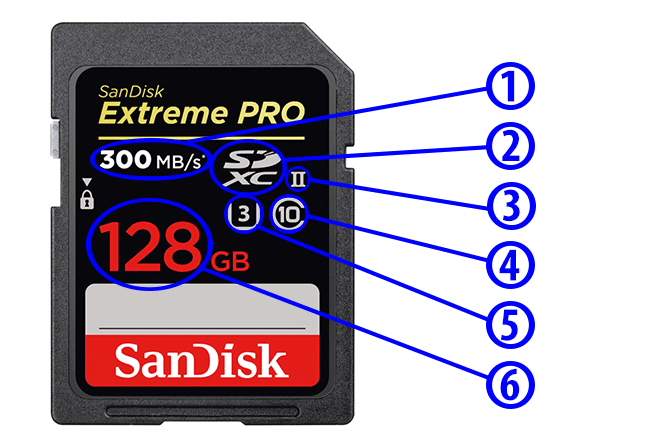
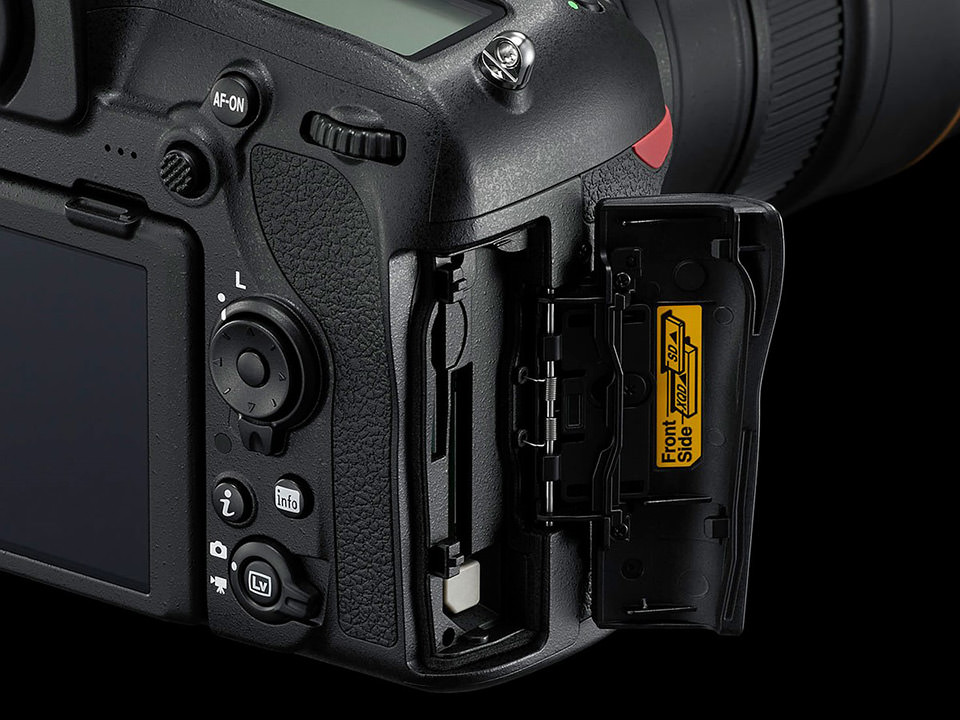
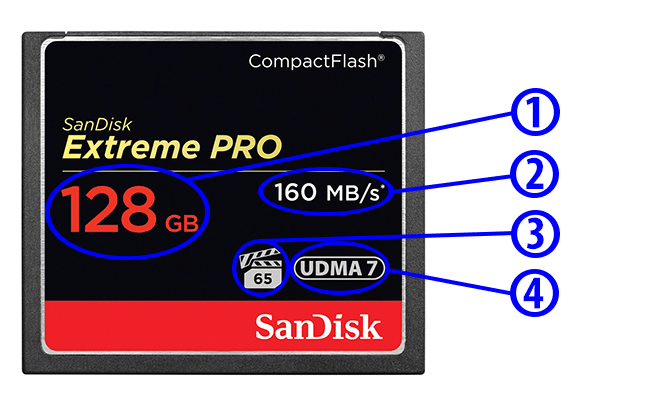


تعليق